How to create a Multilingual website, why is it needed and how good is it for SEO?
Dear, friends! I am delighted to greet you today and would like to tell you a little about multilingual websites. This article is just a small piece of what awaits you when developing and optimizing a multilingual website.
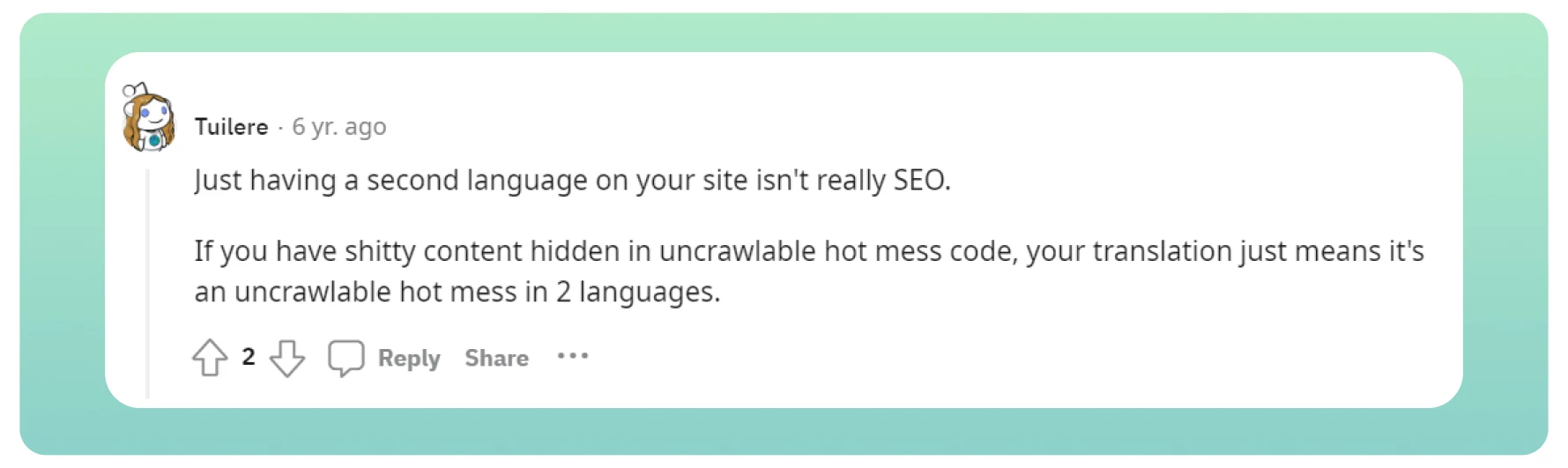
There is a great comment on Reddit that we have saved for this day.
It perfectly conveys that simply translating content and adding a second, third, or even fourth language to your website does not make it SEO-optimized for your site.
Yes, multilingual trends are constantly changing, but as with any other technical aspect, there is a certain foundation that needs to be known and understood first.
Therefore, in this article, we will first go through the key stages and then discuss modern trends and case studies that can be used in your SEO strategy.
So why and who needs multilingualism?
Let’s start with the fact that not every business needs a multilingual website. No matter how much you want to attract more traffic from other regions or countries — it is worth accepting that multilingualism should be justified by something. Constant support for multilingual content requires a lot of time and effort, so multilingual websites are most often created by large B2B companies. News resources, online stores, and blogs are less likely to have multilingual sites.
Before we look at a couple of interesting cases, let’s consider possible ways to implement multilingualism. We will focus only on Google, so we will refer to official documentation.

And what about terminology?
In the field of search engine optimization and website development, there are two terms:
Multilingual website — a website that contains content in multiple languages without being region-specific. For example, if you have an auto repair and detailing service in Germany, your website can be implemented in two languages, English and German. Your website still technically remains in the region of Germany, but now SERP can promote relevant queries in two languages.
Multiregional website — a website that not only contains multilingual content but also has the ability to recognize the region first. These sites have a more complex structure. Let’s change the example, you have an online store for car chemicals that you sell throughout Europe. Now a multiregional website is used, which first recognizes the region, for example, Spain, and within the region, it already contains several languages, Spanish and English. The situation is the same with Germany — the region is different, but there are also two languages, German and English.
How does this look for the search engine?
Assuming that all technical aspects have been met, crawlers consider your site in all regions for the keywords you promote. This significantly increases incoming traffic. After all, you are now present in SERP in two countries and in two languages in each.
Another point, on the Google Webmasters documentation page, you can find a table with methods for managing languages on your resource.
Let’s consider the first three options, as the fourth format is slowly but surely becoming outdated from URL formats.
Purchase of regional top-level domains (ccTLDs)
Purchase of regional top-level domains (ccTLDs)
The first and most obvious way is to buy top-level domains. An excellent and recognizable example is the fast food restaurant KFC (Kentucky Fried Chicken). Just everyone’s favorite chicken restaurant uses the structure of different domains.
**********
Russia — https://www.kfc.ru/
Canada — https://www.kfc.ca/
Great Britain — https://www.kfc.co.uk/
Germany — https://www.kfc.de/
**********
Advantages
The first advantage is the simplicity of technical implementation. It may be that certain types of businesses have different requirements depending on the country where commerce takes place. For example, different requirements for implementation platforms, legal aspects, etc. In reality, each of your domains is a separate site with its own content.
The second advantage of the method is user trust due to a familiar domain. Unlike various subdomains or subdirectories, which are not always understandable to people — everything is simple. The letters after the dot in the site name are your regional affiliation, easily recognized by the naked eye. Essentially, you immediately answer questions from the section — “Do you deliver to my country?”.
Disadvantages
The first advantage, which involves separate websites, is also the first disadvantage. All the resources and efforts you put into a website in Germany will not affect the promotion of your website in Canada at all. This means that you will have to plan a budget for SEO optimization separately for each region.
The second disadvantage can be anticipated, but it is still quite understandable — high costs. As mentioned earlier, increasing the number of websites directly affects your budgets and the number of your own SEO specialists or third-party contractors.
In addition, if you did not take care to buy domains in advance, you may encounter a very unpleasant situation after your first domain becomes successful and your business thrives — cunning brokers will buy similar regional domains and sell them to you at three times the price.
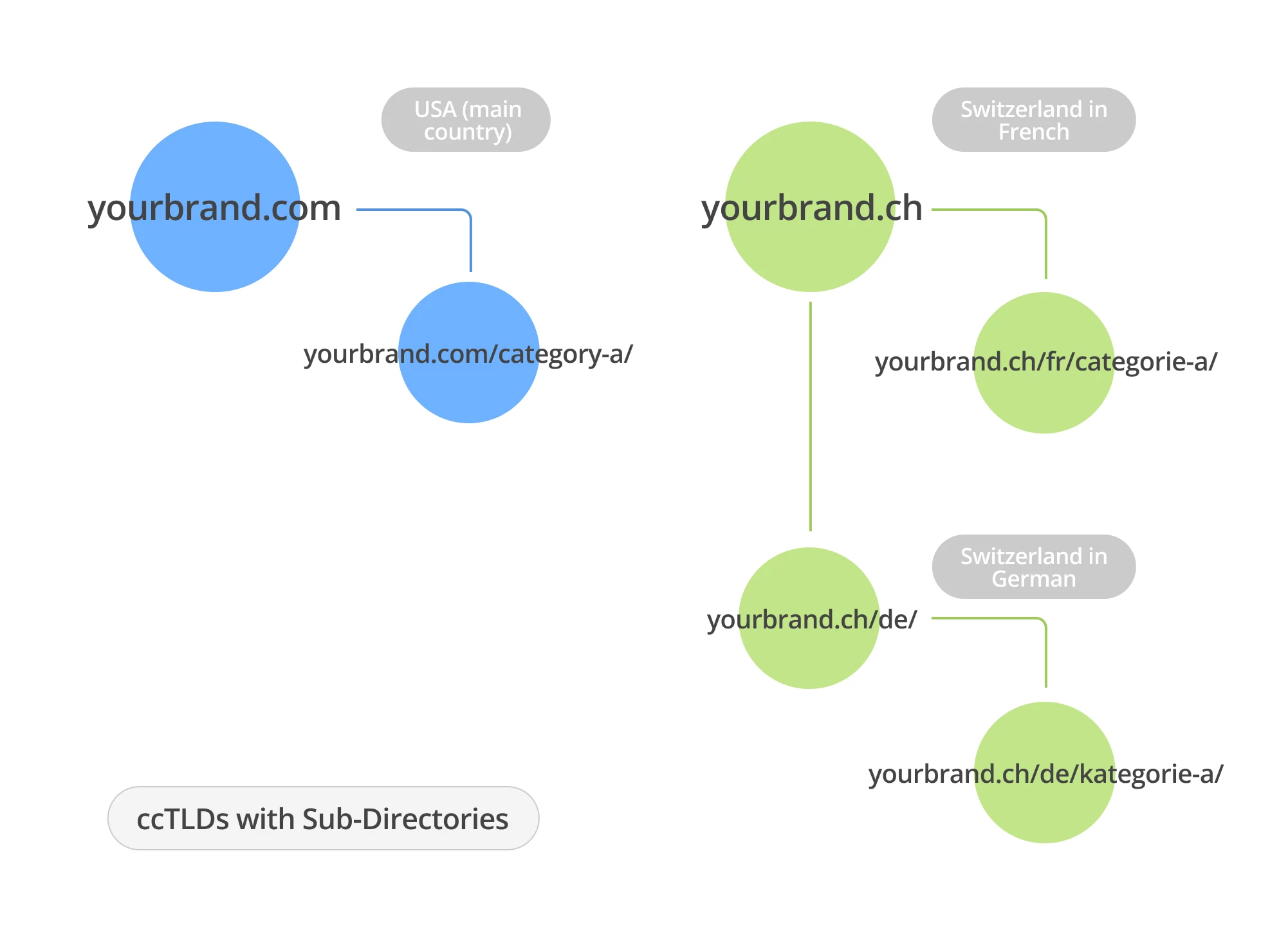
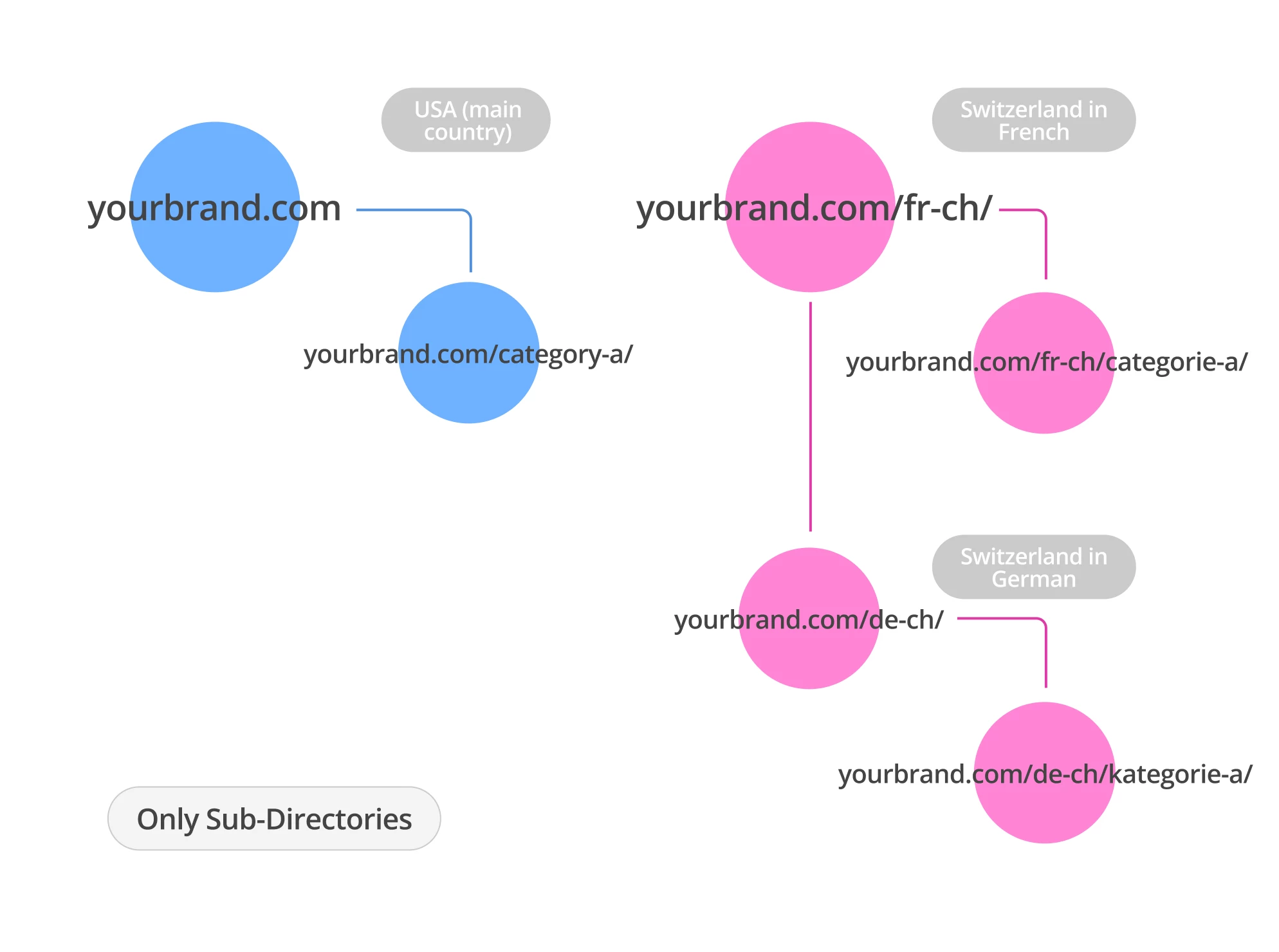
Various subfolders under regions (subfolders with gTLD)
The second implementation method, which you have probably seen more than once. One of the brightest examples can be the website of a well-known company from Cupertino.
Here’s what the URL looks like for different regions:
Germany — https://www.apple.com/de/
Canada — https://www.apple.com/ca/
France — https://www.apple.com/fr/
Great Britain — https://www.apple.com/uk/
And here’s what the URL looks like for Canada, but in French:
This applies to any regions where there will be more than one localization. If you delve into the technical part of the implementation, each region or region+language combination has its own section on the website. In the example above, ISO codes were used, but you can use any names you like as long as your users understand them. However, ideally, it is best to match the name to the one you will use in the ahreflang tag.
Advantages
Unlike the first option with separate domains, in this case, all language versions of the pages exist within one website. This means that all actions aimed at SEO optimization within one localization will in one way or another affect others. For example, an optimized page in French for Canada can have a great impact on the page in French for France. There is one more plus, any of your link building will also spread throughout the entire site.
Disadvantages
As for the disadvantages, it’s not all that straightforward either. The entire codebase will be within one resource, so if any region has “special” requirements, it will become a bit more difficult to fulfill them.
The second issue is that the same server is used for all localizations of the site. The site loading speed from nearby regions will be much faster, but remote regions will experience significant delays when consuming content. To solve this problem, we recommend using a CDN (there will be a separate article on this topic soon).
**********
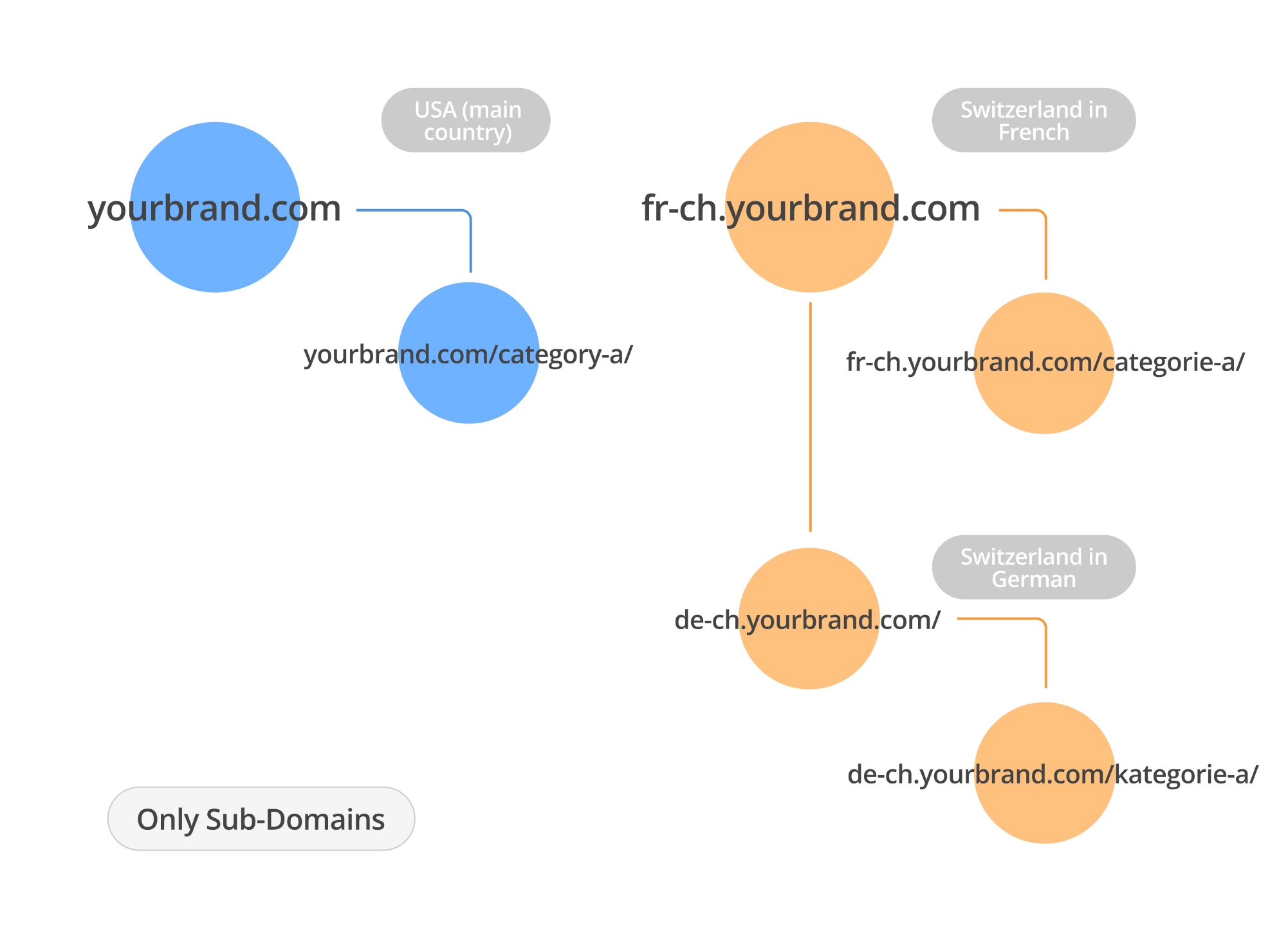
Using Subdomains (subdomains with gTLD)
And finally, the last example is creating subdomains for a country/localization. Here’s what it looks like using the example of a global sports apparel brand.
https://de.shop.gymshark.com/ — Germany
https://uk.shop.gymshark.com/— Great Britain
https://fr.gymshark.com/— France
Implementing subdomains is easier than creating separate first-level regional domains, but it doesn’t provide the same SEO benefits as subfolder-level optimizations.
Advantages
One advantage of this method is that all you need to implement it is access to your domain provider account. In essence, the method is almost identical to purchasing regional domains by structure. If you decide to use this method, it will not be difficult to separate such URLs into different addresses.
Disadvantages
Due to the high similarity with the first method, the disadvantages are almost identical:
- Limited SEO effectiveness, as each subdomain is essentially a separate website with its own language. However, subdomains are still not considered the same domain by search engines;
- If multiple languages are planned for the region, a separate subdomain must be created for each language.
We have looked at three options for implementing URL structures for multilingual websites. But which one should you choose in the end?
It’s simpler than it seems. If you represent a large international corporation, you can implement the option with separate top-level domains. For very large companies, this is the best prospect for scaling business online.
In any other case, we recommend using subfolders. It is a simple implementation and a simpler SEO strategy that is so necessary for small businesses. Remember that subfolders will be hosted on the same server, which can cause delays in content consumption for users from distant regions. If you want everything to be done for you, welcome to outsourcing with us!
**********
Hreflang Tag
In the text above, we have already mentioned the hreflang tag several times. When working with international SEO, this tag will become an integral part of your life. Hreflang is a tag for indicating the country and language on the page for search engines. On each individual page of your resource, you can set linguistic and regional binding of the page.
Here is what the structure looks like:
In country-language-code — indicate the ISO code of the region or combinations of region and language. For example, Canada — can, while Canada in French would be can-fr. Alternative-url — the URL of the page with the specified country and language code.
Before looking at examples of how to write the tag, let’s simulate a situation. You have website pages that you need to promote in France, the United Kingdom, and Germany.
Here’s what the URL will look like:
- https://www.test.com/en/uk –for the United Kingdom
- https://www.test.com/fr/fr –for France
- https://www.test.com/fr/fr –for France
By doing this, you force the search engine to index the page for a specific region and language. To be specific, imagine that you are a large distributor of home products. You have two regions with the same language — the United Kingdom and Australia. The difference between the two pages is only in the prices and contact information of the store. By using this tag, search engines will not consider almost identical content as duplicates.
What else is worth knowing when working with hreflang?
1. The tag is only necessary for working with multilingual content. If you work in one country and in one language, it is not necessary to write hreflang.
2. Hreflang can be used not only for subfolders within one domain but also for different regional domains.
3. Don’t forget to specify the page itself next to the list of alternative pages.
4. The alternative URL must always be complete, including https:// and the domain name. Don’t use relative URLs in hreflang, even if the page you’re linking to is on the same domain.
5. The hreflang tag works only with a bilateral link. Both pages must point to each other, otherwise, the method will not work.
6. Remember that the method only works with ISO codes for countries and languages. You can find them at the following links: countries, languages. Note: the hreflang tag only works if the language code is specified. The tag will not work simply with the country code!
7. If you have ready-made content for England, the United States, and Canada, you can also use it for other English-speaking countries. For example, Australia and Ireland. We specify the code as in the example below, and voila!
Here’s how we set up for the remaining English-speaking countries:
8. Don’t forget to set the value of x-default. The tag is responsible for countries where you have not yet worked or do not plan to localize. Do you think that the majority of your audience understands English? Specify an English language page!
9. An alternative to specifying localization in HTML can also be in the sitemap (sitemap.xml):
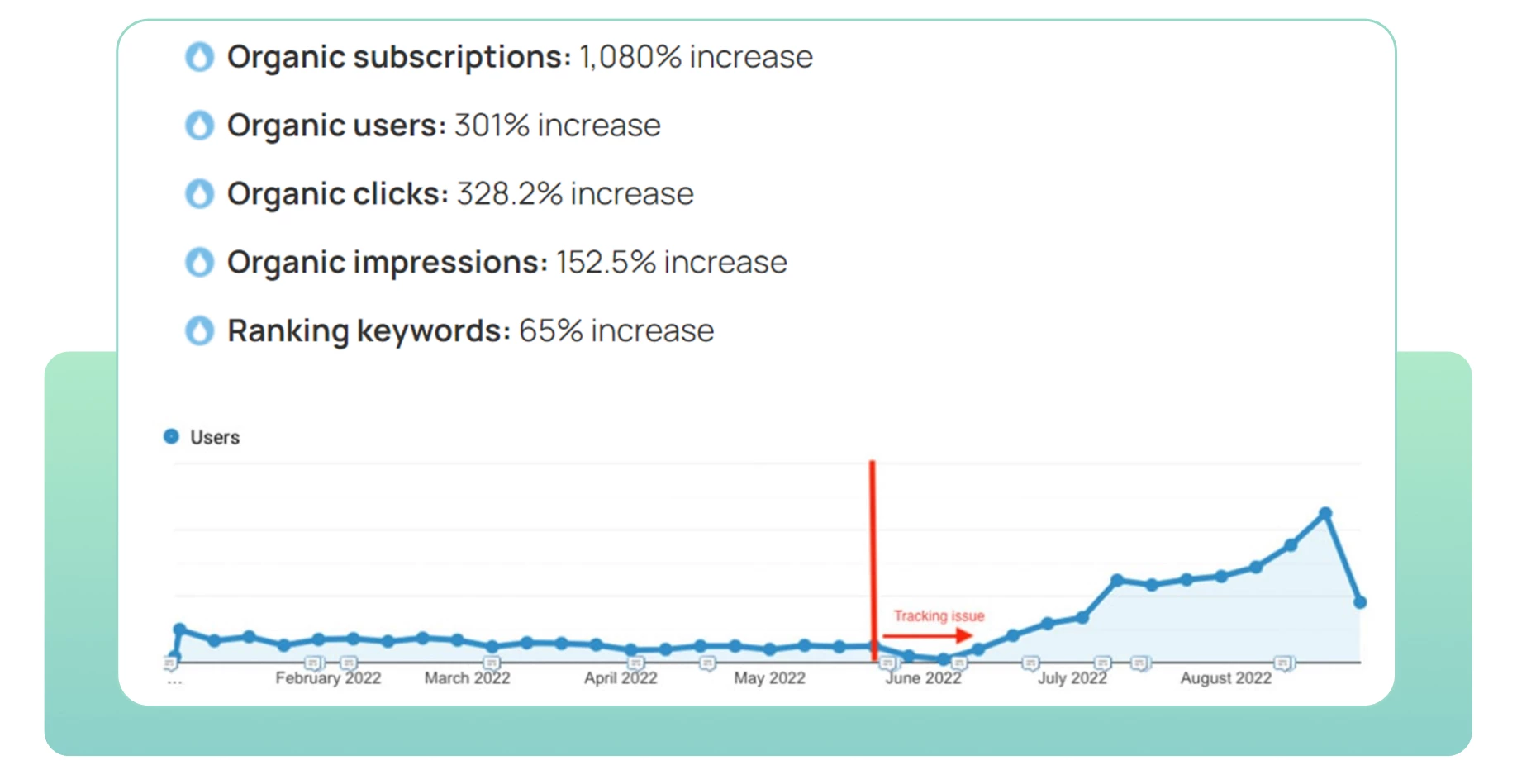
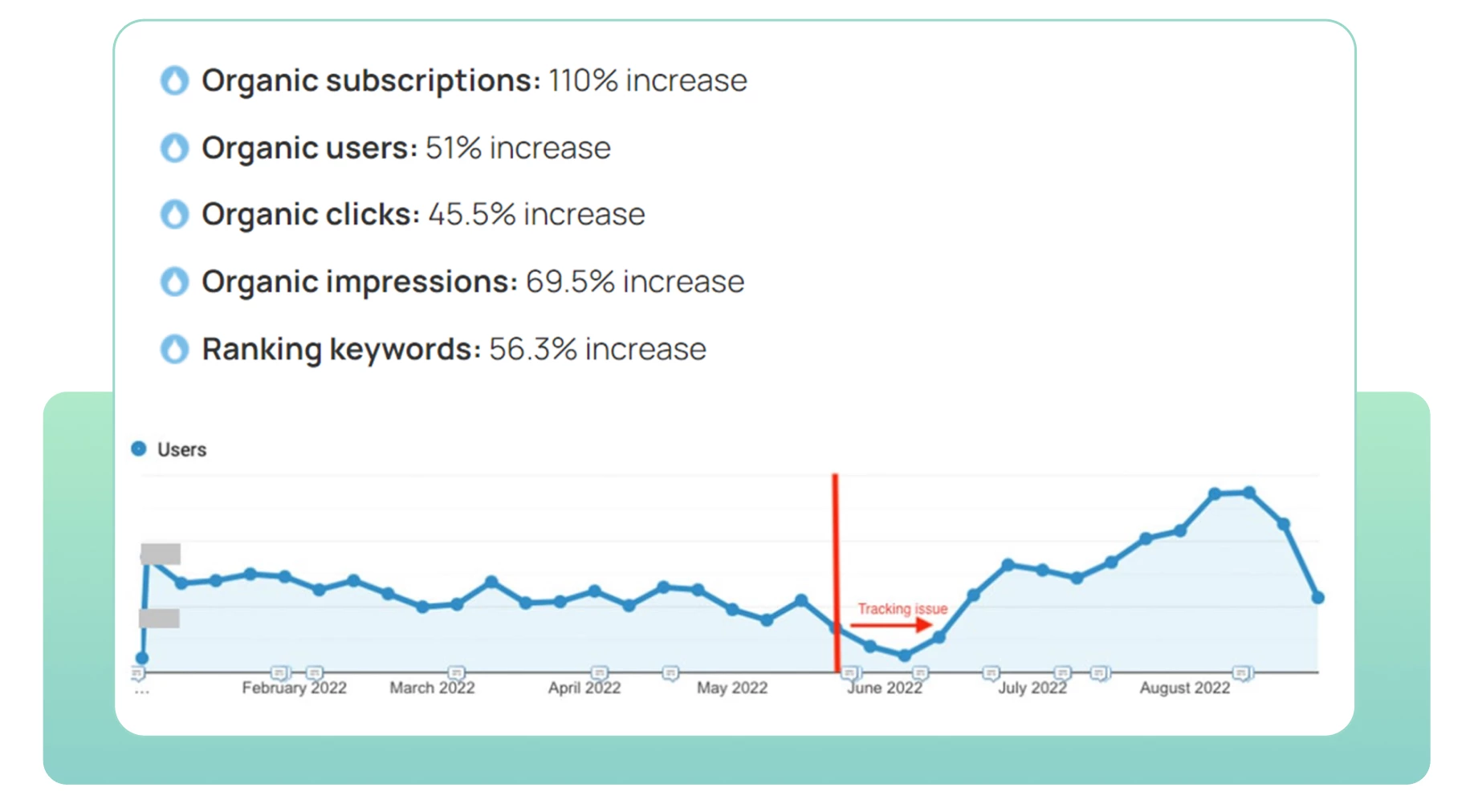
Interesting growth case study
Gaia — yoga video service
Let’s describe an interesting experience of our Western colleagues in promoting a video service with lessons and various videos on yoga.
What was done?
- Subfolders were created for Spain, Germany, and France;
- All ahreflang tags were formed and added for localized content;
- ● Problems with site migration from the previous contractor were resolved;
- Semantic core was prepared and content was prepared for SEO;
- Based on a large number of requests regarding various series and video lessons related to seasons, their specificity was taken into account for SEO, and pagination was also added.
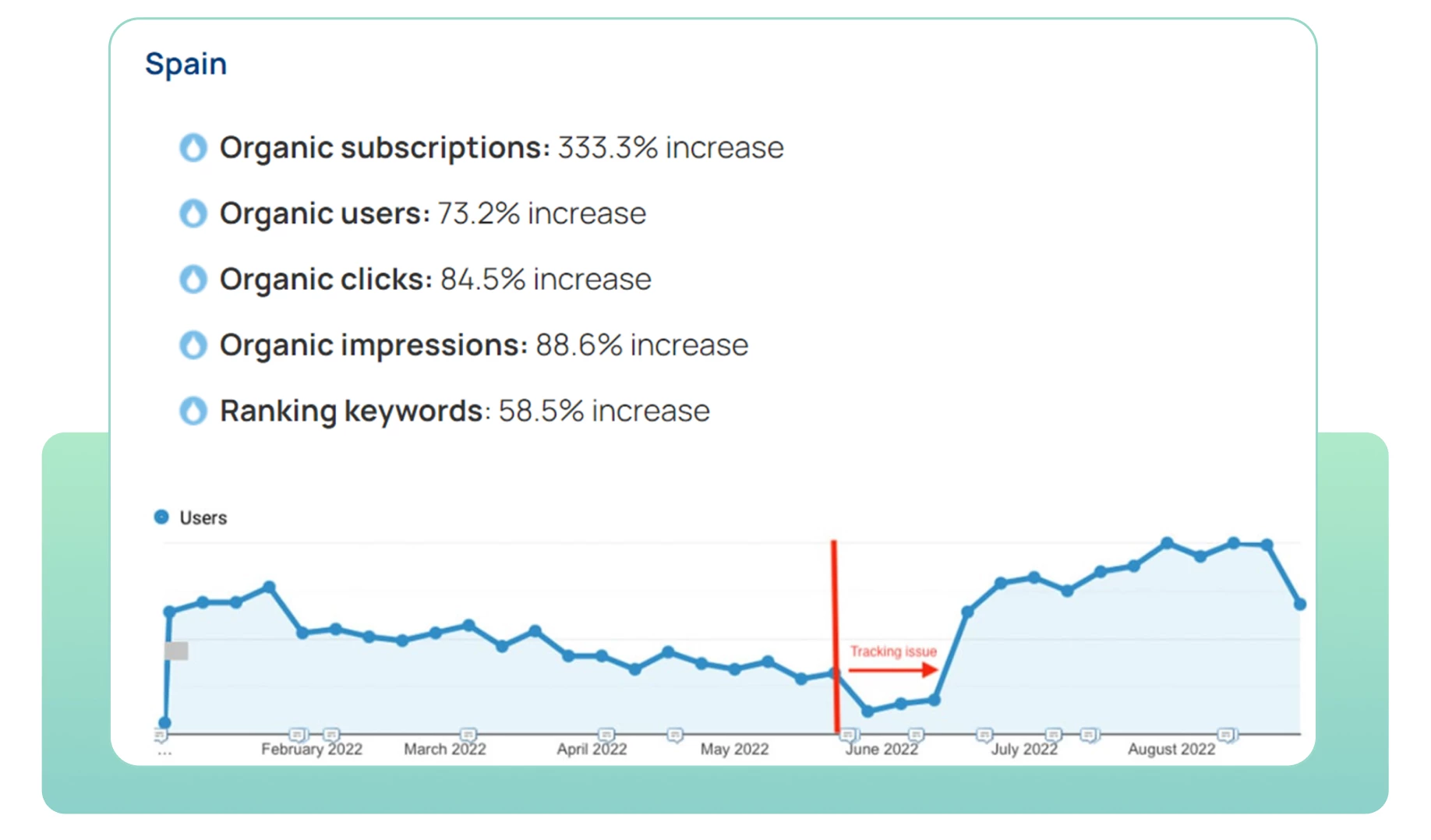
What’s the result? A great one!
Organic subscriptions from other regions increased by 41%, and the total amount of user traffic increased by 3.3%. (All data without taking into account the main country — the U.S.)
Conclusion
If your business is targeting the international market and you have not yet included multilingual and multiregional SEO strategy, you are losing your potential traffic.
Just look at the numbers of market giants, they surely know how important it is to use the opportunities provided by search engines.
- More than 60% of Apple’s sales come from the international market.
- Ford sells 36.7% of its cars on the international market.
- Alphabet also sells more than 50% on the world stage.
- And even a giant like Walmart sells 23% of its sales worldwide.
International SEO is your key to increasing organic traffic to your website from all over the world. If you are ready to grow and scale your business, be sure to use this opportunity.
Dear friends, thank you for reading! I hope it was interesting and most importantly, useful for you!